Virtual reality is reshaping the manufacturing industry by offering many benefits that can help companies significantly reduce downtime costs. It’s become a must-have tool providing solutions to many of the long-standing problems manufacturers face globally. VR is a game changer because it simplifies production processes and workforce training. It has proved helpful by establishing its authority in various applications across many industries, from virtual simulations to enriching safety protocols and employee experiences.
This blog explores the significant benefits of VR in manufacturing, showcasing how companies are leveraging this technology to address key challenges and unlock new opportunities.
According to experts, virtual and augmented technologies will revolutionize how things are built. Virtual Reality shows promise in leveraging development and operational change within the manufacturing industry. Moreover, as organizations evolve in a world tailored towards technology, VR is not an option but a necessity. This is not just about technology but a change in paradigm on how manufacturing activities can be envisioned, performed, and improved.
Manufacturing is a field that thrives on innovation because of its constant need for improvement and adaptation. VR in industrial training offers new possibilities in manufacturing by reimagining traditional processes through immersive experiences. VR today is not just for improving efficiency; it’s about redefining how manufacturers approach design, production, and workforce development.
Design, test, and perfect a product without building multiple physical prototypes. That’s what VR brings to the table. As mentioned above, VR is not just about making things more efficient—it changes everything in manufacturing altogether. From detailed design to training employees and optimizing production lines, VR is making things possible that were beyond comprehension a few years ago.
Gone are the days when physical prototypes were the only option for developing and testing new products. Traditional prototyping required multiple physical iterations, substantial material costs, and extensive manual labor. VR has broken up this paradigm by fostering manufacturers to create detailed virtual prototypes that can be tested and refined quickly without physical limitations.
Companies like Ford and Boeing have initiated VR prototyping, exhibiting remarkable improvements in design cycles. By creating immersive 3D environments, engineers can manipulate complex designs in real-time, downsizing prototype development time by up to 60%. This approach eradicates material waste, reduces production delays, and lowers development costs.
Virtual testing is a massive advancement in product development. It allows engineers to subject virtual prototypes to various stressors, such as temperature fluctuations, pressure, and wear and tear. Aerospace and automotive industries have reported up to 75% reduction in physical testing requirements through comprehensive VR simulation technologies.
These virtual environments capture intricate details of material stress, mechanical interactions, and performance parameters. Engineers can observe how components respond under various conditions, predict potential failure points, and optimize designs before manufacturing a single physical component. This ensures that products meet industry standards and perform reliably in real-world conditions—without needing physical testing environments.
Geographic barriers have traditionally restrained collaborative design processes. VR technologies create shared digital workspaces where global teams can simultaneously interact with design models, regardless of physical location. A design engineer in Detroit can collaborate in real-time with colleagues in Tokyo, manipulating 3D models, discussing modifications, and making instant adjustments.
This global, instantaneous collaboration dramatically reduces communication delays, accelerates decision-making processes, and ensures consistent design quality across international teams.

Manufacturers can use VR to simulate entire production lines and workflows. This allows them to create digital twins of entire production environments, identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or potential points of failure before implementing physical changes.
Manufacturers like Toyota have utilized VR simulations to redesign factory layouts, achieving up to a 30% improvement in production line efficiency. These innovations highlight how digital transformation in manufacturing empowers managers to experiment with different configurations, test workflow scenarios, and make data-driven decisions without risking actual production interruptions.
Traditional factory floor planning relied on 2D blueprints and physical measurements. VR transforms this approach by providing immersive, interactive spatial planning tools. Managers can walk through virtual factory layouts, assess equipment interactions, analyze worker movement patterns, test configurations for equipment placement, workflow paths, and storage solutions. Optimizing these elements virtually leads to better space utilization and enhanced productivity.
Manufacturing training has traditionally been high-risk, expensive, and inconsistent. VR-based training solutions address these challenges by creating safe, repeatable learning environments. Employees can practice complex machinery operations, learn complicated procedures, and develop muscle memory without endangering themselves or risking equipment damage.
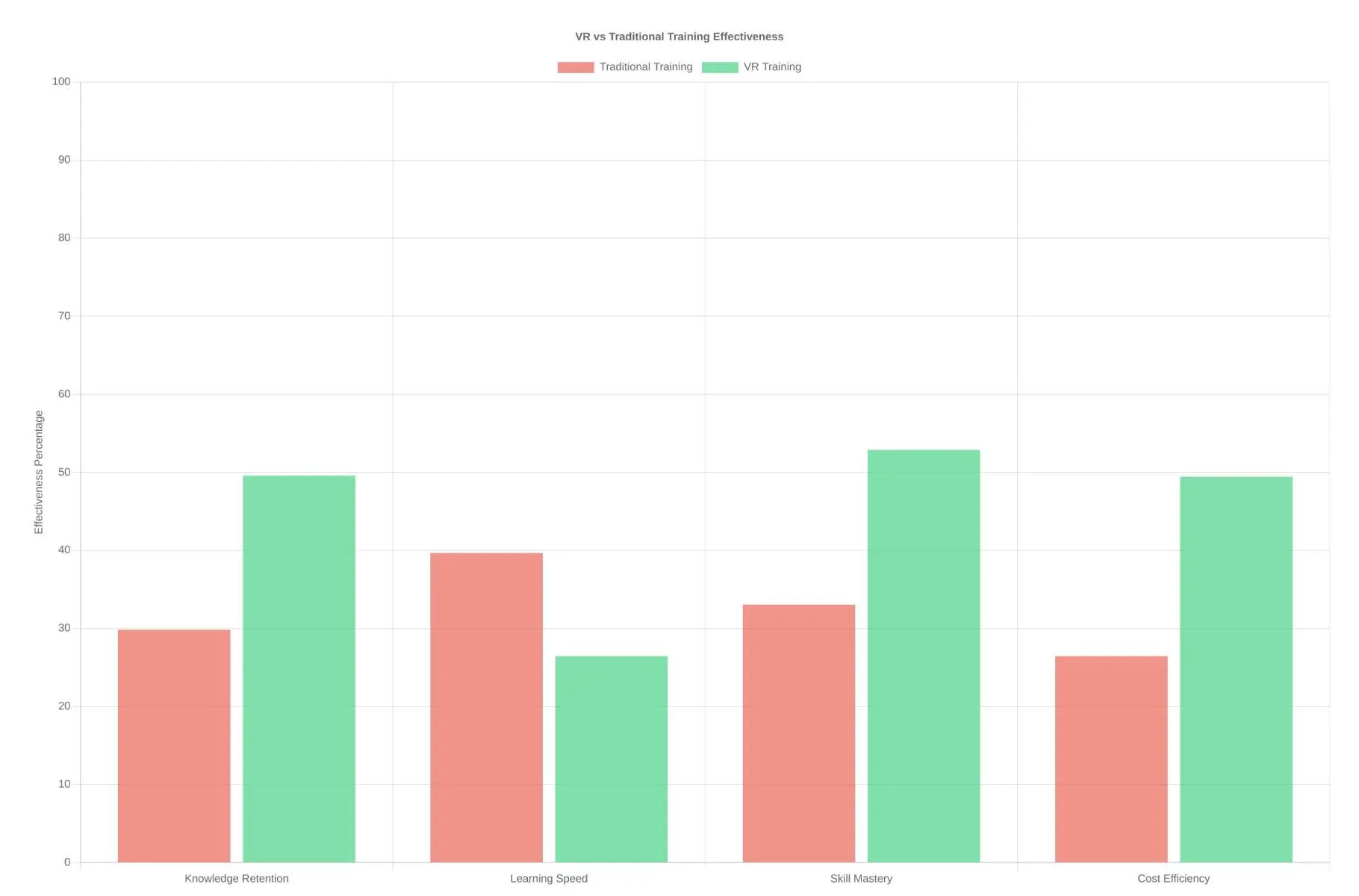
Research shows that VR training can decrease learning time by 40% while increasing knowledge retention by 75%. These aren’t marginal improvements—they represent a fundamental transformation in workforce skill development.
Safety remains a critical concern in manufacturing environments. VR-based training solutions allow employees to experience and respond to hazardous scenarios in controlled, risk-free environments. From chemical spill responses to emergency equipment shutdowns, workers can develop critical safety skills without exposing themselves to actual risks.
VR technologies deliver substantial economic benefits by reducing physical prototyping costs, minimizing training expenses, and optimizing workflow efficiencies. For example, Boeing’s use of VR smart glasses reduced wiring assembly times by 25%, showcasing the financial advantages of virtual tools.
Manufacturing downtime represents one of the most significant financial challenges for manufacturers. A single hour of production blockage can cost companies thousands or even hundreds of thousands of dollars. Virtual Reality is a transformative technology that systematically addresses and minimizes these costly disruptions through innovative industrial VR solutions.
Traditional maintenance procedures have been essentially reactive—waiting for equipment to fail before taking corrective action. This method produces unexpected production halts, significant repair costs, and significant productivity losses. Virtual Reality revolutionizes maintenance protocols by introducing proactive, data-driven intervention strategies.
Digital twin technologies create exact virtual replicas of manufacturing equipment, capturing every minute operational detail. These sophisticated simulations integrate real-time sensor data, historical performance metrics, and predictive algorithms to forecast potential equipment failures before they even occur. Manufacturers can now visualize microscopic wear patterns, simulate stress scenarios, and develop targeted maintenance interventions.
Companies like Siemens and General Electric have pioneered these VR-enabled predictive maintenance systems, reporting up to a 40% reduction in unexpected equipment downtime. By identifying potential failure points through immersive digital simulations, these innovations exemplify how digital transformation in manufacturing enables technicians to schedule precise maintenance windows, minimizing production interruptions and extending equipment lifecycle.
Geographic limitations have traditionally complicated equipment maintenance and troubleshooting processes. When specialized technicians are required to diagnose complex machinery issues, travel costs, response times, and logistical challenges can result in prolonged production stoppages. With VR and Augmented Reality (AR), manufacturers can provide technicians with real-time remote support from experts.
For instance, a technician facing an issue on the factory floor can wear AR-enabled VR glasses, allowing an off-site expert to guide them through the repair process.
This reduces the need for expert travel, accelerates problem resolution, and ensures minimal disruption to production schedules. Manufacturing organizations have documented response time reductions of up to 60% using VR-enabled remote assistance technologies.

Manufacturers can experiment with workflow adjustments through VR simulations and identify potential challenges in a virtual environment. Whether it’s rearranging equipment or introducing a new production line, these simulations ensure changes are implemented smoothly, avoiding unnecessary downtime.
Automotive manufacturers like Toyota have utilized VR workflow simulations to redesign production lines, achieving up to 35% manufacturing efficiency with VR and significantly reducing unexpected disruptions.
Human error represents a substantial contributor to manufacturing downtime. Inadequately trained personnel can cause equipment mishandling, improper maintenance procedures, and operational mistakes that result in prolonged production stoppages. VR solutions for manufacturing offer immersive, risk-free learning environments where employees can develop critical skills without risking actual equipment damage. These training simulations provide:
Research demonstrates that VR in industrial training can reduce skill acquisition time by 40% while improving knowledge retention by 75%. By leveraging this technology, manufacturers can substantially mitigate human-error-related downtime risks and ensure workforce competency through advanced training methodologies.
Integrating Virtual Reality into manufacturing downtime reduction strategies represents more than a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental reimagining of operational resilience. By combining predictive technologies, remote collaboration tools, workflow optimization, and advanced training methodologies, VR enables manufacturers to transform potential disruptions into opportunities for continuous improvement.

Manufacturers can showcase their products in virtual showrooms, enabling customers to interact with and explore products from anywhere in the world. This immersive experience enhances buyer confidence and reduces the need for physical showrooms.
Customers can use VR to visualize customized products in real-time, ensuring their specifications meet their expectations before production begins.
While the benefits of VR are clear, implementing this technology requires careful planning. Common challenges include:
VR facilitates seamless collaboration among geographically dispersed teams. Engineers, designers, and decision-makers can meet in virtual environments, enabling real-time feedback and faster approvals.
Juego Studios is a Virtual Reality Development Company that delivers tailored VR solutions for manufacturing. Whether you’re looking to enhance training programs, optimize factory workflows, or implement predictive maintenance tools, we have the expertise to bring your vision to life. Our cutting-edge applications empower manufacturers to stay competitive while unlocking the full potential of VR.
Virtual Reality is not just a technology of the future; it’s a transformative tool redefining the present. By integrating VR into their processes, manufacturers can speed up product development, enhance workforce training, optimize workflows, and minimize costly downtime. As industries evolve, VR offers a pathway to greater efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.
Now is the time to embrace VR and take your manufacturing operations to the next level.
Virtual Reality (VR) technology revolutionizes maintenance practices by facilitating predictive maintenance and workflow optimization. Technicians can use VR to identify potential equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs. This predictive maintenance is achieved through VR simulations that allow technicians to virtually inspect machinery and identify wear and tear, anomalies, or other potential problems that might not be immediately visible during a standard visual inspection.
Furthermore, VR enables the creation of realistic simulations of workflows, allowing for optimizing processes before implementation in the real world. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and ensures smoother, more efficient operations. By virtually testing different methods and identifying potential bottlenecks, organizations can streamline their maintenance strategies and reduce the risk of unforeseen issues.
Virtual Reality (VR) technology offers significant cost reductions in several key areas. Firstly, it eliminates the expensive and time-consuming process of creating physical prototypes. Instead of building multiple physical models for testing and refinement, companies can design and test prototypes virtually in a VR environment, saving significant resources.
Secondly, VR enhances training efficiency by providing immersive and interactive simulations. This allows employees to practice real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled environment, leading to faster learning curves and improved skills retention without incurring costs associated with real-world training, such as equipment damage or potential injuries.
Thirdly, VR facilitates predictive maintenance by allowing technicians to virtually inspect equipment and identify potential problems before they cause costly downtime. Through VR, maintenance procedures can be simulated and optimized, leading to proactive maintenance and reduced operational disruptions. This minimizes the overall cost associated with unplanned repairs and production losses.
Integrating new technologies into existing manufacturing processes is possible, but it requires meticulous planning and selecting appropriate tools to guarantee seamless compatibility with current systems. This involves thoroughly assessing the existing infrastructure, including machinery, software, and workflows. Careful consideration must be given to data formats, communication protocols, and potential integration points.
The right tools, including specialized software, hardware interfaces, and customized programming, are essential for bridging the gap between the new technology and the established manufacturing environment. Success hinges on a well-defined implementation strategy that addresses potential challenges proactively and minimizes disruption to ongoing operations.
Virtual reality (VR) technology is significantly impacting several major industries. The automotive industry uses VR for designing and testing vehicles, allowing engineers to visualize and interact with 3D models before physical prototypes are built. This saves time and resources. Aerospace companies employ VR for pilot training simulations, providing realistic flight scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. Electronics manufacturers utilize VR for optimizing product design and assembly line, improving efficiency and reducing errors. Finally, heavy machinery manufacturers use VR to train operators on complex equipment, enhancing safety and productivity. These industries are experiencing considerable benefits from the application of VR.
Virtual reality (VR) technology offers a revolutionary approach to safety training. It creates immersive and interactive simulations where workers can rehearse responses to hazardous situations without real-world risks. This means employees can practice handling dangerous equipment, responding to emergencies, or navigating potentially unsafe work environments within the virtual world’s safety. This method allows for repeated practice and refinement of skills, leading to improved safety performance on the job.
The VR training environment can be meticulously designed to reflect a particular workplace’s specific hazards and challenges, providing highly targeted and relevant training. This targeted approach significantly enhances the effectiveness of safety training compared to traditional methods.
VR provides realistic simulations designed to enhance skill retention and boost employee confidence. VR for industrial simulations significantly reduces the onboarding time required for new hires to reach full proficiency in their roles. The improved skill retention is achieved through repeated practice in a safe, simulated environment. This allows new employees to learn from mistakes without real-world consequences, thus improving their confidence levels and reducing the time it takes them to master their job tasks. The faster onboarding process leads to increased productivity and cost savings for the company.
Virtual Reality (VR) is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by significantly improving efficiency and fostering innovation. This is achieved by implementing smarter workflows, enhanced training programs, and predictive maintenance strategies. Smarter workflows leverage VR to visualize and optimize production lines, allowing for identifying and resolving bottlenecks before they impact production.
Improved training uses immersive VR simulations to train employees on complex machinery and procedures in a safe and controlled environment, reducing the risk of errors and accidents on the factory floor. Predictive maintenance, facilitated by VR, enables technicians to visualize and diagnose potential equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This proactive approach allows manufacturers to schedule maintenance efficiently and prevent costly breakdowns.